LQG: Inverse Optimal Control for Continuous Psychophysics
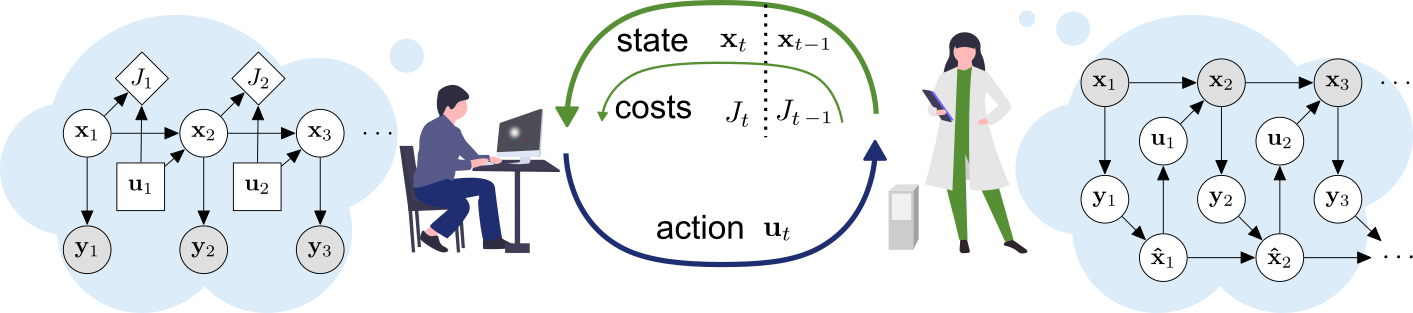
This repository contains the official JAX implementation of the inverse optimal control method presented in the paper:
Installation
The package can be installed via pip
python -m pip install lqg
Since publication of our eLife paper, I have substantially updated the package. If you want to use the package as described in the paper, please install an older version <0.20:
python -m pip install lqg==0.1.9
If you want the latest development version, I recommend cloning the repository and installing locally in a virtual environment:
git clone git@github.com:dominikstrb/lqg.git
cd lqg
python -m venv env
source env/bin/activate
python -m pip install -e .
Usage examples
main.pyshows how to simulate data and infer parameters using the LQG model of the tracking task.notebooks/Tutorial.ipynbexplains the model and its parameters in more detail, including the extension to subjective internal models (based on my tutorial at CCN 2022)
Citation
If you use our method or code in your research, please cite our paper:
@article{straub2022putting,
title={Putting perception into action with inverse optimal control for continuous psychophysics},
author={Straub, Dominik and Rothkopf, Constantin A},
journal={eLife},
volume={11},
pages={e76635},
year={2022},
publisher={eLife Sciences Publications Limited}
}
Extensions
Signal-dependent noise
This implementation supports the basic LQG framework. For the extension to signal-dependent noise (Todorov, 2005), please see our NeurIPS 2021 paper and its implementation.
Non-linear dynamics
We are currently working on extending this approach to non-linear dynamics and non-quadratic costs. Please check out our NeurIPS 2023 paper and its implementation.



